A Beginners Guide to Optimize Your Website Source Code for SEO (2022 Noobs are welcome)
Every marketing expert understands the significance of SEO in the age of digital technologies. But, if you're on a marketing team and have only a basic understanding of SEO, what do you need to know to create your first effective SEO campaign?
Sean Work aims to convey all you need to know about the principles of SEO in 45 minutes in this webinar. He talks about how to optimize your site, develop content, and drive traffic to your site.
Sean was formerly an SEO manager at Advantage Marketing Consulting Services, which supplied search marketing services to Fortune 500 firms including Thomson Reuters and Samsung.
When considering SEO, keep the following points in mind:
- Don't expect SEO to be the main engine of your business.
- You have no influence over Google, but you do have control over what appears on your website.
Understand thy source code!
This is how the source code appears:
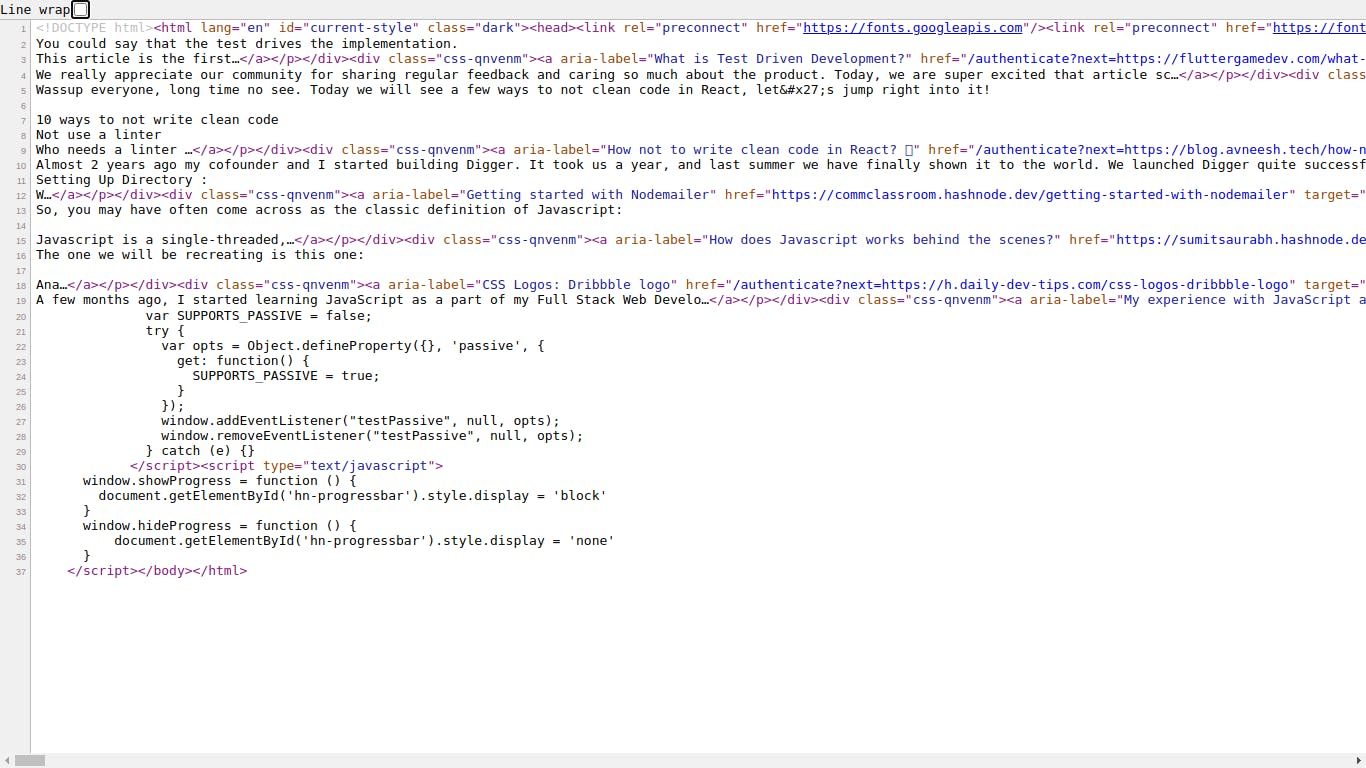
You may find something like this in the source code of any web page. The source code is not frightening. It is just the code that web browsers "read" to determine how to display the contents of a web page. Google and other search engines scan your source code to determine the topic of your site.
Go to a web page and perform one of the following (depending on your browser):
CTRL + U on a computer
On a Mac or on Chrome: View > Source > Developer
Google How to Use on Safari
Title tag
The most significant element on every web page is the title tag. You may see the title tag in the source code by pressing 'Control + U' on any page. It is defined by title tags.

Make sure that each page only has one title tag. What you write in the title tag is how Google chooses what will appear in search engine results.
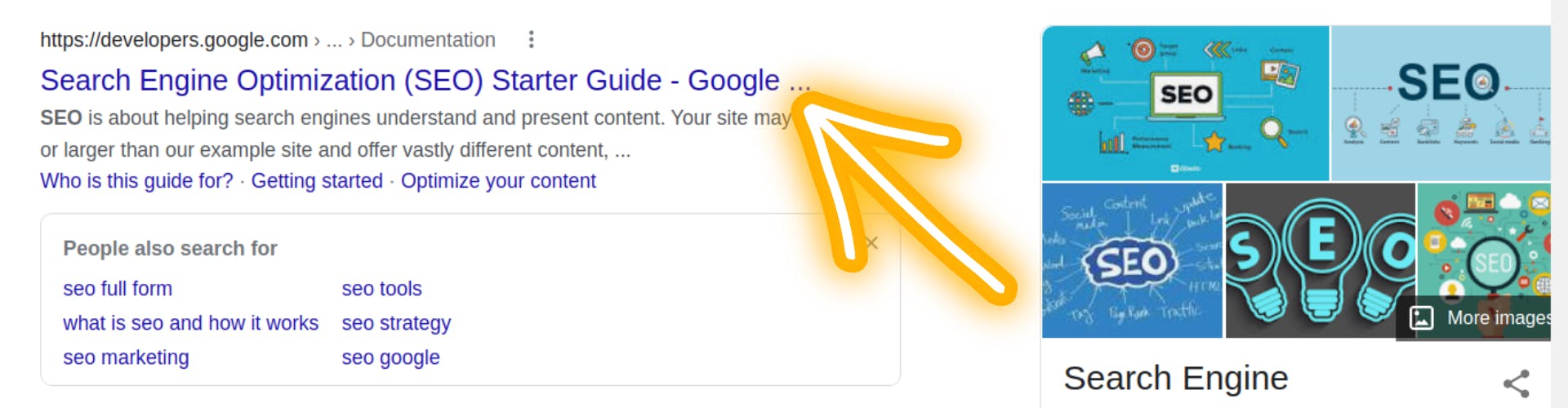
Google has been experimenting with modifying this little, but most of the time they duplicate precisely what's in your title tag onto the search engine web page, so it's critical that you build your title tag such that it reads good and people click on the link.
Many individuals will advise you to include your most crucial keywords in this tag, but be cautious. You don't want to become preoccupied with keywords. You want it to be effortless. Describe the page and write it as if you were a copywriter.
One thing to consider is how you would write this if you were creating an advertisement for a brochure. The more organically it is written, the more likely it is that people will click on it.
Meta description
The meta description is the following item in any web page code, and it looks like this:
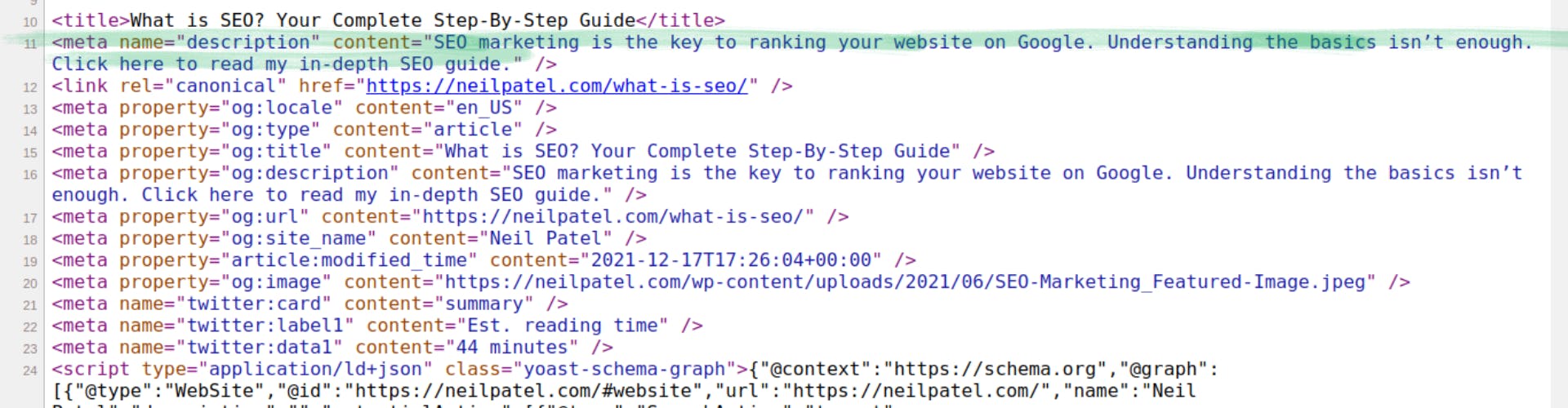
This is yet another piece of code in the page's header. There is just one of these. This is the page's description. You can go into further depth on what the page is about. Many businesses neglect this step and wind up replicating their homepage meta description material on every page.
Google Search Console informs these businesses that there are several duplicate descriptions. It has no effect on your search ranking and isn't a major issue, but you're sabotaging your chances of receiving free advertising.
The meta description, as you can see, is the second piece of material or language beneath your title tag. This is some free advertising provided by Google that you should take advantage of. People read it, and this is how they decide whether or not to click on your link to view your content. Consider what you want to include in your meta descriptions.
The H1 heading tag
The H1 heading tag is another piece of code you have, and it looks like this:

The H1 header is the page's primary heading. When they click through and read your material, you should produce text that is warm and appealing. This is another step in integrating the rest of the content. The H1 header is intended to make readers think, "Wow, I'd really like to read the remainder of this page." Some folks used to simply copy the title tag information into the H1, which is OK. However, you might want to have something a little more interesting, something more specialized for that page that makes more sense after they arrive.
This is crucial since Google looks at these, so avoid keyword stuffing on this page. Simply make it look natural and inviting.
Anchor text and internal links
How internal connections and anchor texts function is a crucial fundamental. There will be connections to any information on any web page. This is how the code for any link looks.

This can go to a link on your site or another website. Another essential point to note is that the anchor text is included within the material nested by this element.
The anchor text in the above example is "This is a link to my website." The words in the anchor text are a highly crucial factor that search engines consider. It assists them in determining what that page will be about, and they utilize it in their algorithm to determine what your entire site is about and which pages they should display to their users. Many individuals employ keyword stuffing to influence it. Keep in mind that internal links and anchor text should be natural and readable.
Nofollow hyperlinks
The "nofollow" property is used within anchor links:

This anchor link is a little more tricky because it contains some JavaScript, but don't be put off by it. Sean has clearly defined rel='external no follow'. You may just use rel="nofollow." The "nofollow" property instructs Google and other search engines not to follow the link to the next page and to disregard it when calculating link juice. When you employ nofollow, you are telling Google that you do not want them to focus on the link to the following page. You want to point Google toward items you believe are more significant.
You should basically just use this for blog comments to reduce spam because people frequently provide links to other sites.
To keep these spamming individuals at bay, the "nofollow" tag was introduced. People used to associate the "nofollow" element with page sculpting, which implies you try to guide your link juice to specific portions of the site that they want you to focus on. You should avoid this behavior and only use it for editing purposes and in blog comments. Check out Google's documentation for more information on nofollow and when to use it.
Alt tags for images
Another crucial tag is "image alt," which is very significant in e-commerce.
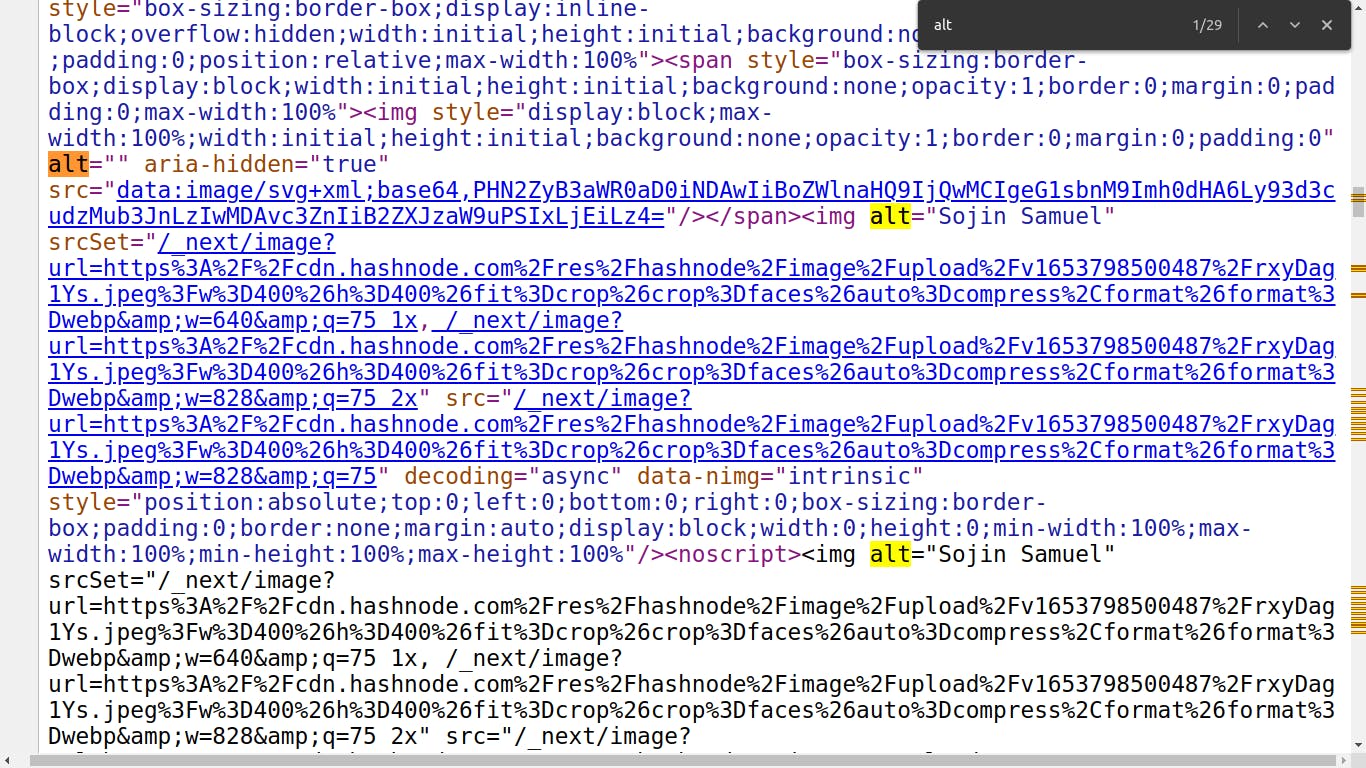
This tag informs a search engine about the subject of a picture. The graphic in the example is about lead management, as you can see. This is how robots like Google understand your image, and it helps your image rank better in image searches.
Image alt tags should not be used for ornamental pictures. Make use of them for:
- Merchandise images
- Diagrams
- Infographics
- Your site's logo
- Screenshots
- Team members' photos
... as well as other areas where it is acceptable. Consider your picture alt tag as follows: What words would you use to describe your image to someone who couldn't see it?
Canonical tag
The "canonical tag" is a tag that was introduced in 2009:

It's significant because if you have a number of web pages with identical information, you can tell Google that the only page they should focus on is a certain page. This is an effective method for preventing duplicate material. This is also significant for syndicating your material since syndicators can include this tag in the head of the page they're taking from you and linking back to you as the original source. Canonical tags are handy for specifying a preferred URL for your content.
Ending
SEO is vital in today's digital world, and while you can't control what Google does, you can improve your website's rating in search results.
Spending effort generating the proper tags and code for your site will reward you with increased visitors and improved search rankings.
What steps have you taken to optimize the source code of your website?